Tapered Thread for Pipes (R Thread)
Tapered pipe threads (pipe tapered threads) are sealed threads and are functionally designed to prevent leakage. However, in order to completely prevent leakage, anti-leak tape or sealant is usually wrapped around the surface of the thread. The thread mountain shape is rounded, and the tooth mountain angle is 55°, distributed on 1/16 tapered pipes. In the ISO 7-1 standard, the male thread is marked R and the female thread is marked Rc. German DIN 2999, Japanese JIS B 0203, British BSP Tr and other standards are set with reference to ISO 7-1. PT is the specification name of the old JIS standard. Simply put, R = PT = BSPT.
The angle and shape of the tapered thread for pipes are the same as those of the parallel thread G(PF) for pipes, so it is practically feasible to use G(PF) female threads with R(PT) male threads. The angle between the peak and the mountain of NPT tapered threads for pipes made in the United States is different from that of tapered threads for pipes R(PT) thread, cannot be mixed.
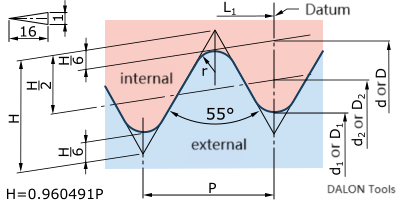
Thread Specifications
- Thread Angle: 55° (Rounded profile)
- Standard: ISO 7-1, DIN 2999
- Type: Sealing tapered thread
- Application: Pipe connections (R = PT = BSPT)
R Thread Specifications
| Name of Thread | Thread per Inch | Pitch P | Major Diameter D, d | Median Diameter D2, d2 | Minor Diameter D1, d1 | Pitch Radius R | Base Length L1 |
|---|
Important Note
Base Length: Since the thread diameter on the cone surface will change with position, an imaginary base plane is defined as a reference for the major diameter, middle diameter, and minor diameter. The distance between this surface and the external thread end face is called Datum length.
FAQ
- What is the difference between R and NPT tapered threads?
R threads have a 55° angle with rounded profile following ISO 7-1 standards, while NPT threads have a 60° angle with sharp profile following ANSI/ASME B1.20.1. Both use 1/16 taper but are not interchangeable due to different angles. - Why are R threads considered "sealing" threads?
The 1/16 taper creates a wedging action as threads are tightened, compressing the thread flanks together to form a metal-to-metal seal. This design is specifically intended to prevent leakage in pressurized systems. - What does R = PT = BSPT mean?
These are different names for the same thread standard: R (ISO designation), PT (old Japanese JIS designation), and BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper). They all refer to the same 55° tapered pipe thread with 1/16 taper. - Can R male threads be used with G female threads?
Yes, this is a common and practical combination. R male threads can mate with G female threads because they have the same 55° angle and pitch. The tapered male provides the seal while the parallel female provides support and ease of assembly. - How should I properly install R threaded fittings?
Apply appropriate thread sealant or PTFE tape to the male threads. Hand-tighten until snug, then use a wrench for additional turns (typically 1-4 turns depending on size). The taper will create the seal, but sealant helps prevent leakage and galling. - What are typical applications for R threads?
R threads are used in plumbing systems, hydraulic connections, pneumatic systems, and industrial piping where leak-proof connections are critical. They're particularly common in European and Asian markets following ISO standards.